About external load indices
LSF bases job scheduling and host selection decisions on the resources available within your cluster. A resource is a characteristic of a host (such as available memory) or a cluster that LSF uses to make job scheduling and host selection decisions.
A static resource has a value that does not change, such as a host’s maximum swap space. A dynamic resource has a numeric value that changes over time, such as a host’s currently available swap space. Load indices supply the values of dynamic resources to a host’s load information manager (LIM), which periodically collects those values.
LSF has a number of built-in load indices that measure the values of dynamic, host-based resources (resources that exist on a single host)—for example, CPU, memory, disk space, and I/O. You can also define shared resources (resources that hosts in your cluster share) and make these values available to LSF to use for job scheduling decisions.
If you have specific workload or resource requirements at your site, the LSF administrator can define external resources. You can use both built-in and external resources for LSF job scheduling and host selection.
LSF does not include a default elim; you should write your own executable to meet the requirements of your site.
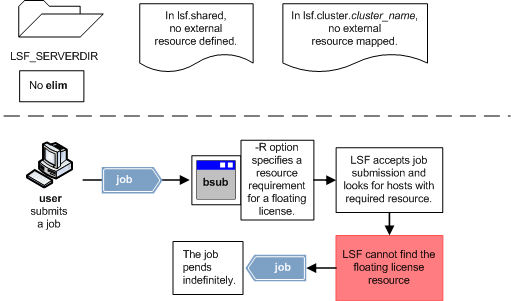
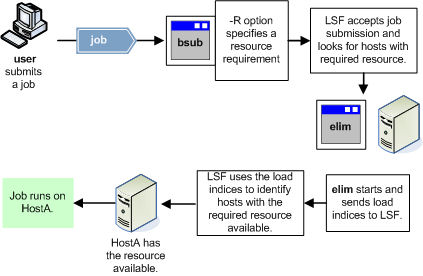
The following illustrations show the benefits of using the external load indices feature.
Default behavior (feature not enabled)
With external load indices enabled
Scope
Applicability |
Details |
|---|---|
Operating system |
|
Dependencies |
|