Resources
Resources are physical and logical entities that are used by applications in order to run. While resource is a generic term, and can include low-level things such as shared memory segments or semaphores, in LSF, EGO manages CPU slots.
A resource of a particular type has attributes. For example, a compute host has the attributes of memory, CPU utilization, operating system type, and so on.
Resource groups
Resources may be grouped together into logical groups to simplify identification, resource allocation, or for administration and monitoring purposes. These resource groups are used to provide a consumer with a like group of hosts to run workload—any host in a resource group should be able to run the same workload.
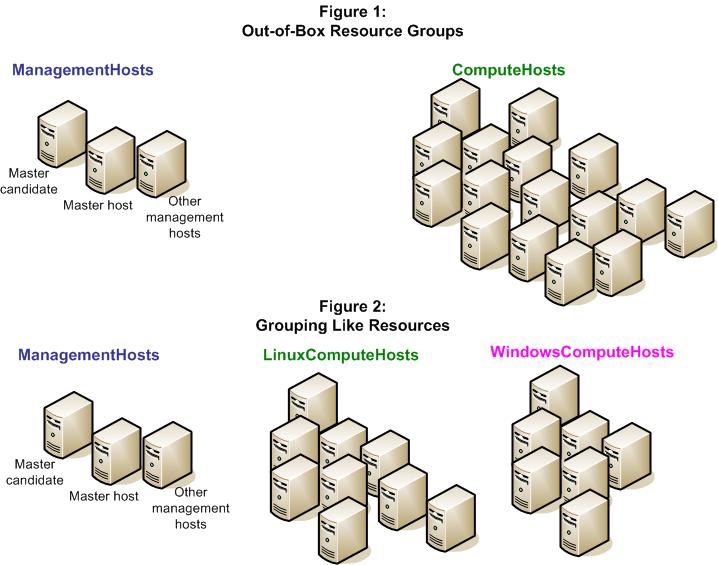
ManagementHosts
ComputeHosts
If all of your hosts are identical, these resource groups may suffice. If your application requires a specific type of hosts (for example, with a minimum processor speed), and not all hosts meet this criteria, you likely need to create resource groups to group like hosts together.
For example, a simple way to group resources may be to group your hosts by operating system type.
EGO provides a common grouping mechanism for resources. Resources may come and go from the system, so EGO supports dynamic membership in a resource group. Hosts can be placed explicitly into individual resource groups, or the resource groups can be defined to have a dynamic membership based on specific criteria. This criteria includes operating system type, CPU speed, total memory, or swap configuration, or custom attributes.