IBM Platform LSF 9.1.3 Quick Reference
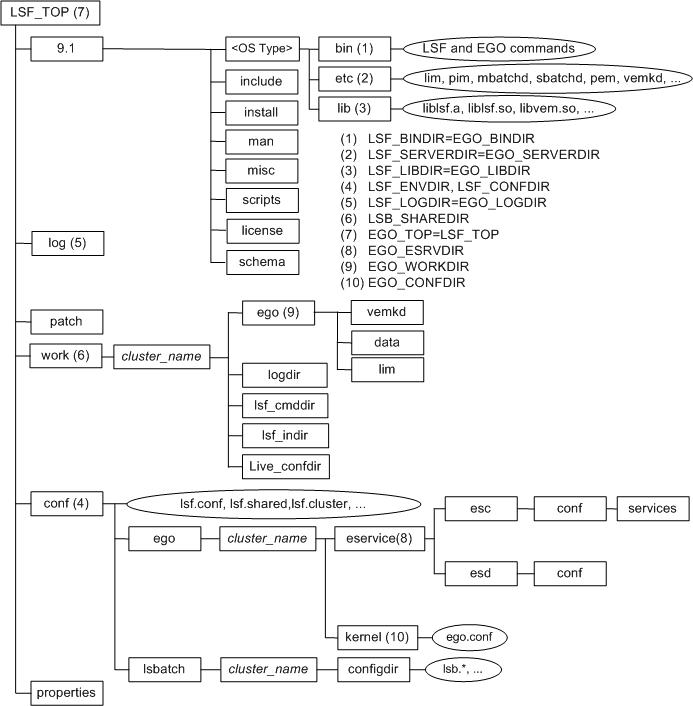
Sample UNIX installation directories
Daemon error log files
Daemon error log files are stored in the directory defined by LSF_LOGDIR in lsf.conf.
LSF base system daemon log files |
LSF batch system daemon log files |
|---|---|
pim.log.host_name |
mbatchd.log.host_name |
res.log.host_name |
sbatchd.log.host_name |
lim.log.host_name |
mbschd.log.host_name |
If EGO_LOGDIR is defined in ego.conf, file lim.log.host_name is stored in the directory defined by EGO_LOGDIR.
Configuration files
lsf.conf, lsf.shared, and lsf.cluster.cluster_name are located in LSF_CONFDIR.
lsb.params, lsb.queues, lsb.modules, and lsb.resources are located in LSB_CONFDIR/cluster_name/configdir/.
File |
Description |
|---|---|
install.config |
Options for LSF installation and configuration |
lsf.conf |
Generic environment configuration file describing the configuration and operation of the cluster |
lsf.shared |
Definition file shared by all clusters. Used to define cluster name, host types, host models and site-defined resources |
lsf.cluster.cluster_name |
Cluster configuration files used to define hosts, administrators, and locality of site-defined shared resources |
lsb.applications |
Defines application profiles to define common parameters for the same types of jobs |
lsb.params |
Configures LSF batch parameters |
lsb.queues |
Batch queue configuration file |
lsb.resources |
Configures resource allocation limits, exports, and resource usage limits |
lsb.serviceclasses |
Defines service-level agreements (SLAs) in an LSF cluster as service classes, which define the properties of the SLA |
lsb.users |
Configures user groups, hierarchical fairshare for users and user groups, and job slot limits for users and user groups |
Cluster configuration parameters (lsf.conf)
Variable |
Description |
UNIX Default |
|---|---|---|
LSF_BINDIR |
Directory containing LSF user commands, shared by all hosts of the same type |
LSF_TOP/version/platform/bin |
LSF_CONFDIR |
Directory for all LSF configuration files |
LSF_TOP/conf |
LSF_ENVDIR |
Directory containing the lsf.conf file. Must be owned by root. |
/etc (if LSF_CONFDIR is not defined) |
LSF_INCLUDEDIR |
Directory containing LSF API header files lsf.h and lsbatch.h |
LSF_TOP/version/include |
LSF_LIBDIR |
LSF libraries, shared by all hosts of the same type |
LSF_TOP/version/platform/lib |
LSF_LOGDIR |
(Optional) Directory for LSF daemon logs. Must be owned by root. |
/tmp |
LSF_LOG_MASK |
Specifies the logging level of error messages from LSF commands |
LOG_WARNING |
LSF_MANDIR |
Directory containing LSF man pages |
LSF_TOP/version/man |
LSF_MISC |
Help files for the LSF GUI tools, sample C programs and shell scripts, and a template for an external LIM (elim) |
LSF_TOP/version/misc |
LSF_SERVERDIR |
Directory for all server binaries and shell scripts, and external executables invoked by LSF daemons, must be owned by root, and shared by all hosts of the same type |
LSF_TOP/version/platform/etc |
LSF_TOP |
Top-level installation directory. The path to LSF_TOP must be shared and accessible to all hosts in the cluster. It cannot be the root directory (/). |
Not defined Required for installation |
LSB_CONFDIR |
Directory for LSF Batch configuration directories, containing user and host lists, operation parameters, and batch queues |
LSF_CONFDIR/lsbatch |
LSF_LIVE_CONFDIR |
Directory for LSF live reconfiguration directories written by the bconf command. |
LSB_SHAREDIR/cluster_name/live_confdir |
LSF_SHAREDIR |
Directory for LSF Batch job history and accounting log files for each cluster, must be owned by primary LSF administrator |
LSF_TOP/work |
LSF_LIM_PORT |
TCP service port used for communication with lim |
7879 |
LSF_RES_PORT |
TCP service port used for communication with res |
6878 |
LSF_MBD_PORT |
TCP service port used for communication with mbatchd |
6881 |
LSF_SBD_PORT |
TCP service port used for communication with sbatchd |
6882 |
Administration and accounting commands
Only LSF administrators and root users can use these commands.
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
lsadmin |
LSF administrative tool to control the operation of the LIM and RES daemons in an LSF cluster, lsadmin help shows all subcommands |
lsfinstall |
Install LSF using install.config input file |
lsfrestart |
Restart the LSF daemons on all hosts in the local cluster |
lsfshutdown |
Shut down the LSF daemons on all hosts in the local cluster |
lsfstartup |
Start the LSF daemons on all hosts in the local cluster |
badmin |
LSF administrative tool to control the operation of the LSF Batch system including sbatchd, mbatchd, hosts and queues, badmin help shows all subcommands |
bconf |
Changes LSF configuration in active memory |
Daemons
Executable Name |
Description |
|---|---|
lim |
Load Information Manager (LIM) — collects load and resource information about all server hosts in the cluster and provides host selection services to applications through LSLIB. LIM maintains information on static system resources and dynamic load indices |
mbatchd |
Master Batch Daemon (MBD) — accepts and holds all batch jobs. MBD periodically checks load indices on all server hosts by contacting the Master LIM. |
mbschd |
Master Batch Scheduler Daemon — performs the scheduling functions of LSF and sends job scheduling decisions to MBD for dispatch. Runs on the LSF master server host |
sbatchd |
Slave Batch Daemon (SBD) — accepts job execution requests from MBD, and monitors the progress of jobs. Controls job execution, enforces batch policies, reports job status to MBD, and launches MBD. |
pim |
Process Information Manager (PIM) — monitors resources used by submitted jobs while they are running. PIM is used to enforce resource limits and load thresholds, and for fairshare scheduling |
res |
Remote Execution Server (RES) — accepts remote execution requests from all load sharing applications and handles I/O on the remote host for load sharing processes. |
User commands
Viewing information about your cluster.
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
bhosts |
Displays hosts and their static and dynamic resources |
blimits |
Displays information about resource allocation limits of running jobs |
bparams |
Displays information about tunable batch system parameters |
bqueues |
Displays information about batch queues |
busers |
Displays information about users and user groups |
lshosts |
Displays hosts and their static resource information |
lsid |
Displays the current LSF version number, cluster name and master host name |
lsinfo |
Displays load sharing configuration information |
lsload |
Displays dynamic load indices for hosts |
Monitoring jobs and tasks.
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
bacct |
Reports accounting statistics on completed LSF jobs |
bapp |
Displays information about jobs attached to application profiles |
bhist |
Displays historical information about jobs |
bjobs |
Displays information about jobs |
bpeek |
Displays stdout and stderr of unfinished jobs |
bsla |
Displays information about service class configuration for goal-oriented service-level agreement scheduling |
bstatus |
Reads or sets external job status messages and data files |
Submitting and controlling jobs.
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
bbot |
Moves a pending job relative to the last job in the queue |
bchkpnt |
Checkpoints a checkpointable job |
bkill |
Sends a signal to a job |
bmig |
Migrates a checkpointable or rerunnable job |
bmod |
Modifies job submission options |
brequeue |
Kills and requeues a job |
bresize |
Releases slots and cancels pending job resize allocation requests |
brestart |
Restarts a checkpointed job |
bresume |
Resumes a suspended job |
bstop |
Suspends a job |
bsub |
Submits a job |
bswitch |
Moves unfinished jobs from one queue to another |
btop |
Moves a pending job relative to the first job in the queue |
bsub command
Selected options for bsub [options] command[arguments]
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
-ar |
Specifies the job is autoresizable |
-H |
Holds the job in the PSUSP state at submission |
-I|-Ip|-Is |
Submits a batch interactive job. -Ip creates a pseudo-terminal. -Is creates a pseudo-terminal in shell mode. |
-K |
Submits a job and waits for the job to finish |
-r |
Makes a job rerunnable |
-x |
Exclusive execution |
-app application_profile_name |
Submits the job to the specified application profile |
-b begin_time |
Dispatches the job on or after the specified date and time in the form [[month:]day:]:minute |
-C core_limit |
Sets a per-process (soft) core file size limit (KB) for all the processes that belong to this job |
-c cpu_time[/host_name | /host_model] |
Limits the total CPU time the job can use. CPU time is in the form [hour:]minutes |
-cwd "current_working_directory" |
Specifies the current working directory for the job |
-D data_limit |
Sets the per-process (soft) data segment size limit (KB) for each process that belongs to the job |
-E "pre_exec_command [arguments]" |
Runs the specified pre-exec command on the execution host before running the job |
-Ep "post_exec_command [arguments]" |
Runs the specified post-exec command on the execution host after the job finishes |
-e error_file |
Appends the standard error output to a file |
-eo error_file |
Overwrites the standard error output of the job to the specified file |
-F file_limit |
Sets per-process (soft) file size limit (KB) for each process that belongs to the job |
-f "local_file op[remote_file]" ... |
Copies a file between the local (submission) host and remote (execution) host. op is one of >, <, <<, ><, <> |
-i input_file | -is input_file |
Gets the the standard input for the job from specified file |
-J "job_name[index_list]%job_slot_limit" |
Assigns the specified name to the job. Job array index_list has the form start[-end[:step]], and %job_slot_limit is the maximum number of jobs that can run at any given time. |
-k "chkpnt_dir [chkpnt_period][method=method_name]" |
Makes a job checkpointable and specifies the checkpoint directory, period in minutes, and method |
-M mem_limit |
Sets the per-process (soft) memory limit (KB) |
-m "host_name [@cluster_name][[!] | +[pref_level]] | host_group[[!] |+[pref_level]] | compute_unit[[!] |+[pref_level]]..." |
Runs job on one of the specified hosts. Plus (+) after the names of a host or group indicates a preference. Optionally, a positive integer indicates a preference level with higher numbers indicating a greater preference. |
-n min_proc[,max_proc] |
Specifies the minimum and maximum numbers of processors required for a parallel job |
-o output_file |
Appends the standard output to a file |
-oo output_file |
Overwrites the standard output of the job to the specified file |
-p process_limit |
Limit the number of processes for the whole job |
-q "queue_name ..." |
Submits job to one of the specified queues |
-R "res_req" [-R "res_req" ...] |
Specifies host resource requirements |
-S stack_limit |
Sets a per-process (soft) stack segment size limit (KB) for each process that belongs to the job |
-sla service_class_name |
Specifies the service class where the job is to run |
-T thread_limit |
Sets the limit of the number of concurrent threads for the whole job |
-t term_time |
Specifies the job termination deadline in the form [[month:]day:]hour:minute |
-v swap_limit |
Sets the total process virtual memory limit (KB) for the whole job |
-W run_time[/host_name | /host_model] |
Sets the run time limit of the job in the form [hour:]minute |
-h |
Prints command usage to stderr and exitse |
-V |
Prints LSF release version to stderr and exits |